
Trimming
What is trimming?
Trimming is frequently adopted in analog or mixed-mode circuit design to provide design options and signal fine tuning.
The circuit design of analog or mixed-mode ICs typically includes specifications that define the parameters for the input and output of analog signals; however, small variations in manufacturing flow can cause the analog signals to deviate from target specifications. The deviations (i.e. circuit mismatch and signal bias) must be corrected or compensated for in applications requiring high precision.
eMemory’s embedded NVM IPs provide a small memory array for storing trimming information within the IC. That information can be used to precisely adjust the input or output signal of the analog circuit.
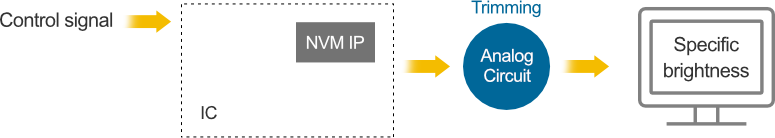
eMemory’s Logic NVM Silicon IP Benefits and Features
eMemory’s logic NVM silicon IPs offer designers the ability to fine tune sensitive signals. Other benefits include:
Testable at Circuit Probe (CP) stage; thus, avoiding yield loss at Final Test (FT), Module, and System stages.
Trimming available at different testing stages, including CP, FT, Module, and System stages.
Smallest silicon IP size for mainstream consumer electronic ICs.
Electronic programming avoids residue contamination of poly/metal fuse.
Support logic, mixed-signal, RF, high-voltage, BCD, SiGe, automotive, and low-power processes.
Silicon-proven at 23 major foundries and available for over 300 qualified processes.
Applications
Parameter Setting
